South Sudan Peace: Lessons That Shaped US Strategy
The journey of South Sudan since its independence has been a crucible for international peace operations, particularly for the United States. South Sudan Peace has become more than a regional concern; it represents a testbed for shaping how Washington approaches complex conflicts. By examining the challenges and outcomes, policymakers can glean vital lessons that resonate far beyond the African continent.
1. The Complexity of Local Conflicts
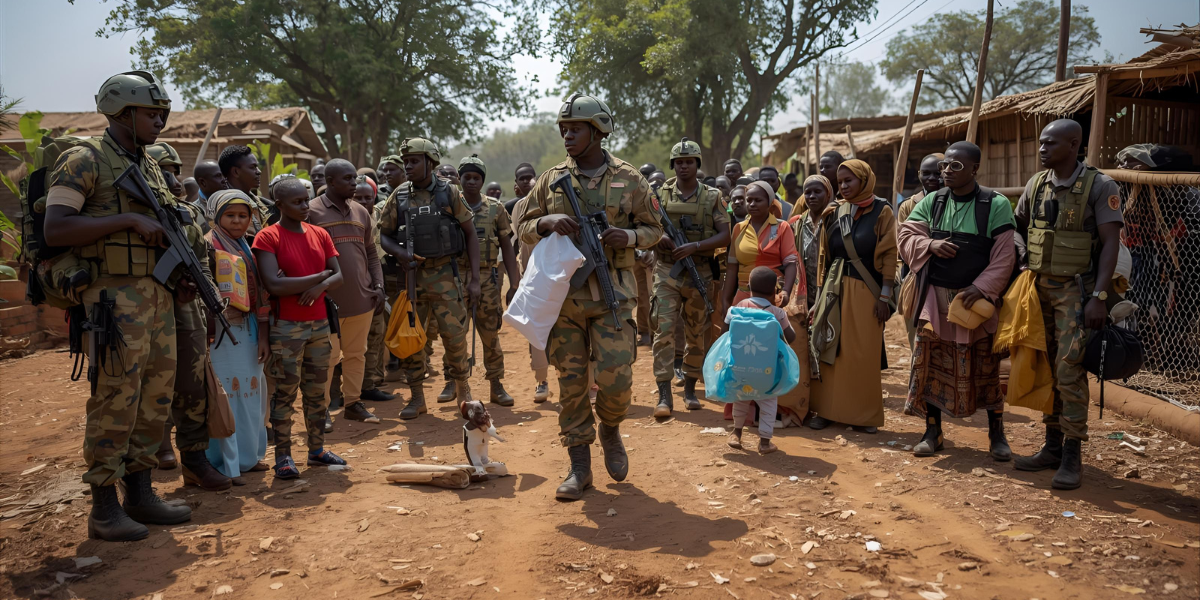
South Sudan Peace demonstrates that local conflicts are rarely isolated. Ethnic divisions, resource struggles, and historical grievances intertwine to create a volatile environment. For U.S. peace operations, understanding these layers is critical. The missteps and successes in addressing localized violence have influenced subsequent strategies in other regions, highlighting the need for nuanced, culturally-informed interventions.
2. The Importance of Diplomatic Engagement
South Sudan Peace emphasizes the pivotal role of diplomacy. U.S. efforts have involved sustained negotiations with multiple stakeholders, including the South Sudanese government, opposition factions, and international partners. Diplomacy has proven that military involvement alone cannot secure lasting peace. The lessons learned here reinforce the importance of patient, persistent dialogue in future peace operations worldwide.
3. Early Warning and Rapid Response
South Sudan Peace reveals the necessity of robust early-warning systems. Swift identification of escalating tensions allows for timely interventions, potentially preventing widespread violence. The U.S. experience underscores the need for integrated intelligence, local monitoring, and coordination with international organizations to act decisively when conflicts ignite. This lesson has shaped rapid response protocols in subsequent peace operations.
4. Coordinating International Support
South Sudan Peace underscores the challenge of coordinating international efforts. The U.S. must work alongside the UN, African Union, and regional actors to ensure coherent strategies. Collaborative planning and resource-sharing prevent duplication and enhance mission effectiveness. For further insights on UN peacekeeping coordination, visit UN Peacekeeping.
5. Balancing Humanitarian and Security Priorities
South Sudan Peace illustrates the delicate balance between humanitarian aid and security objectives. U.S. operations must protect vulnerable populations while fostering political stability. Humanitarian corridors, safe zones, and targeted aid distribution all play a role in mitigating the human cost of conflict. These lessons inform broader policies on crisis response in regions like the Sahel and the Horn of Africa. Explore our detailed analysis on conflict management in Africa here.
6. Learning from Past Failures
South Sudan Peace shows that acknowledging past mistakes is essential. Early miscalculations in troop deployments, negotiation strategies, and resource allocation provided critical feedback for U.S. policymakers. By systematically reviewing failures, lessons are institutionalized, ensuring that future operations avoid repeating the same errors. Continuous learning becomes a cornerstone of effective peace strategy.
7. Strengthening Local Governance
South Sudan Peace highlights the importance of supporting local governance structures. Strong institutions at the community level foster stability and build trust in national leadership. U.S. operations focus on training local officials, promoting transparency, and empowering civil society organizations to create a sustainable foundation for peace. Effective local governance reduces the likelihood of renewed conflict.
8. Leveraging Technology in Peace Operations
South Sudan Peace demonstrates the value of technology. Satellite imagery, mobile reporting, and data analytics allow U.S. forces to monitor conflict zones, track humanitarian needs, and respond faster to crises. Innovative tools improve decision-making and enhance coordination between military, diplomatic, and humanitarian actors, setting a precedent for technologically informed peace missions worldwide.
9. Engaging Regional Partners
South Sudan Peace reveals that engaging regional actors is vital for durable solutions. Neighboring countries influence stability through cross-border trade, migration, and political alliances. U.S. operations benefit from fostering strong regional partnerships, sharing intelligence, and supporting multilateral initiatives. This approach aligns with broader U.S. foreign policy objectives and strengthens peacekeeping capacity across Africa.
10. Preparing for Long-Term Commitment
South Sudan Peace teaches that short-term interventions are insufficient. Lasting peace requires long-term engagement, from diplomatic initiatives to development projects. The U.S. experience emphasizes sustained support for education, infrastructure, and economic growth, ensuring that peace initiatives are not temporary fixes but transformative efforts. Learn more about sustainable peacebuilding strategies at Council on Foreign Relations.
Conclusion
South Sudan Peace has proven to be a defining test for shaping U.S. peace operations policy. From local conflict complexities to long-term strategic commitments, every lesson informs future interventions. By understanding these dynamics, the United States can better navigate international crises, foster stability, and support nations in achieving lasting peace. South Sudan’s journey underscores the critical balance between diplomacy, military strategy, and humanitarian support, offering a blueprint for global peace efforts in the decades to come.